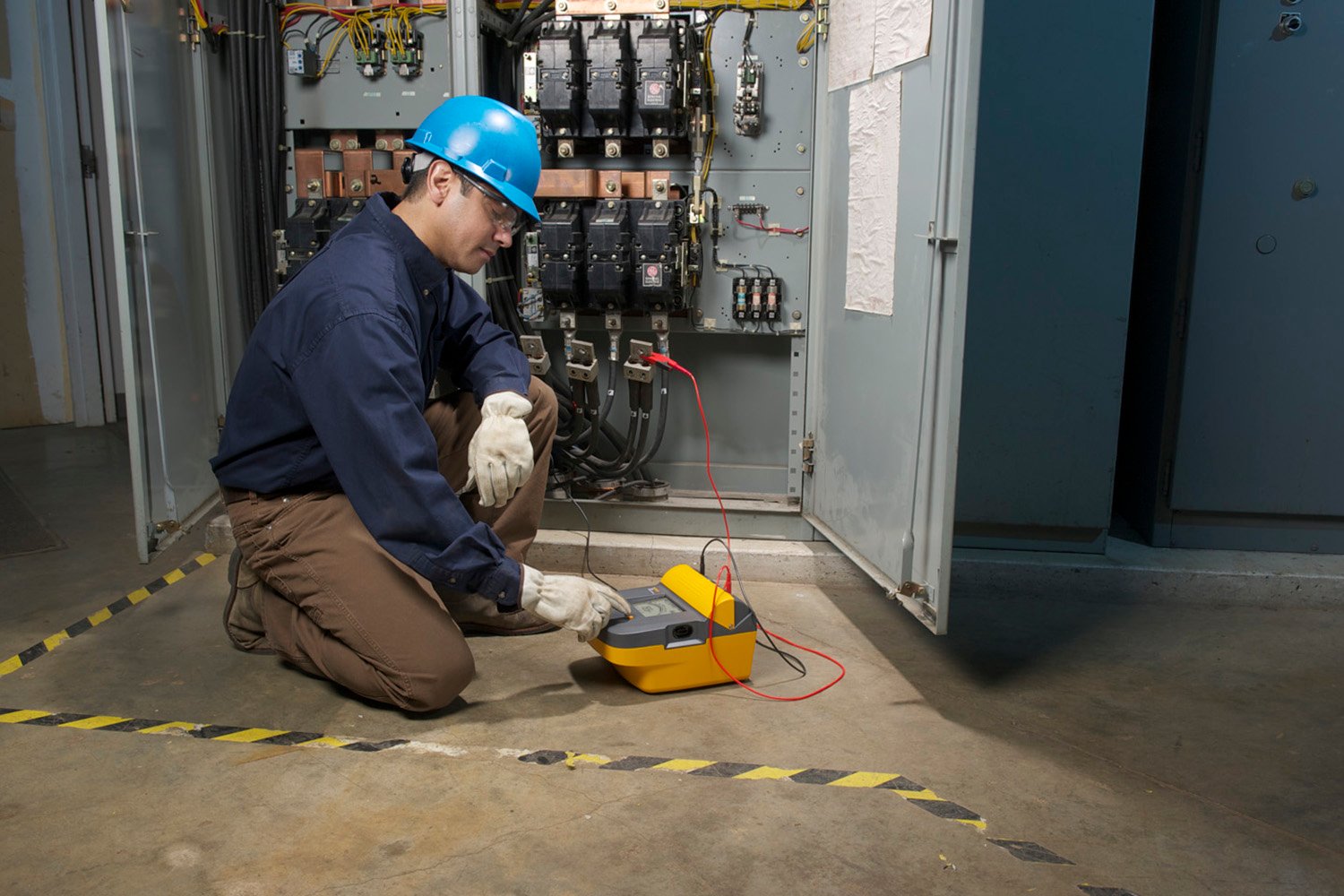
A lot is riding on the shoulders of maintenance managers to keep systems up and running. Their success teeters on the performance of machinery that requires regular attention — electrical systems of motors that run everything from pumps and conveyors, to grinders, HVAC, and fans, among other things.
Every minute down is a loss. Unplanned downtime costs are difficult to calculate, but often significant. For some industries, it can represent 1 to 3 percent of revenue (potentially 30 to 40 percent of profits) annually.
Two common approaches to system maintenance include run-to-fail and preventive.
- In a run-to-fail approach, the motors control system downtime. When a motor fails, it takes time to bring back up and get it running again.
- In a preventive maintenance approach, maintenance managers control system downtime. Motor maintenance is planned, avoiding unnecessary system downtime.
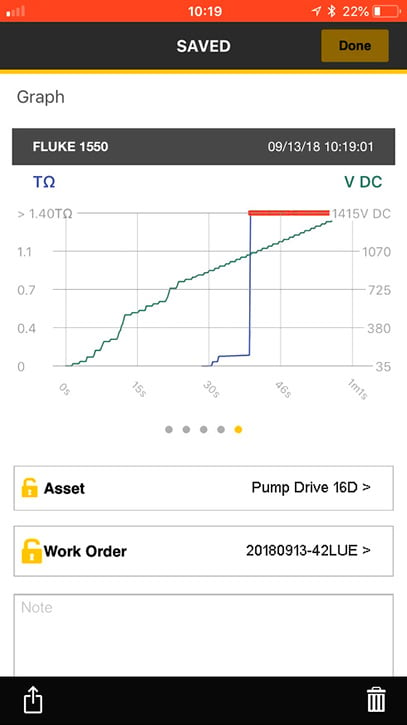
This is an example of a run-to-fail maintenance approach:
- An insulation test was conducted on the motor prior to installation;
- No tests were conducted until after the motor failed; and
- The motor was taken out of service, rewound, tested and reinstalled.
The failure caused an unplanned stop in production. The true cost of this failure was not limited to the cost to repair the motor—up to half the cost of buying a new motor—it also included lost production time and wasted labor costs.
Prevent motor downtime
Periodic motor maintenance tests provide valuable information about the state of insulation deterioration and will help predict a possible failure of the system. Preventing problems will result in a more trouble-free system and extend the operating life of system equipment. Insulation resistance testers can be used to determine the integrity of windings or cables in motors, transformers, switchgear, and electrical installations.
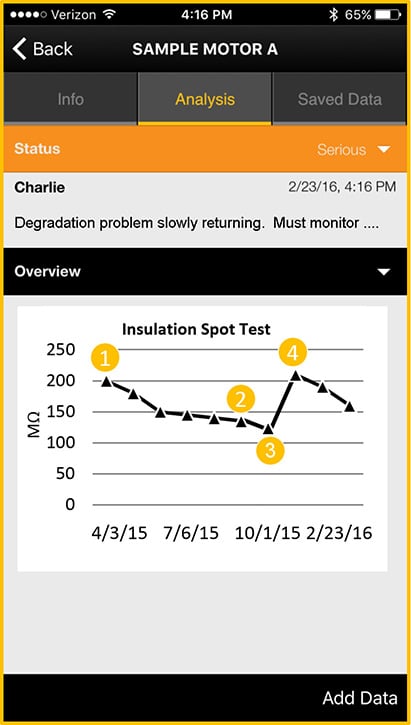
This is what we know about motor insulation: it will deteriorate over time and with use. Deteriorated or damaged insulation leads to current leakage. Current leakage causes undo wear on the motor.
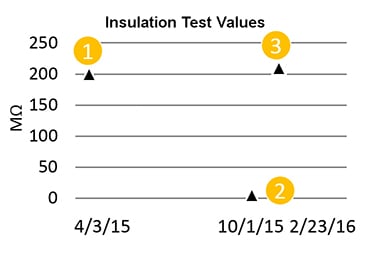
This is the maintenance log for a motor in a preventive maintenance program:
- Insulation tests were conducted regularly;
- The insulation values deteriorated over time;
- Service was scheduled when the resistance value dropped below a predetermined threshold, which allowed for planning downtime in advance; and
- After service, the motor was put back in service, starting a new preventive maintenance cycle, and tested—the insulation test result was better than when record keeping started.
Making it happen
The move from run-to-fail to preventive maintenance includes making decisions about scheduling tests and collecting data. Here are some things to consider:
- Test frequency should be based on the motor’s age and extent of use. Develop a schedule that allows you to test those devices which are most heavily used, and are most critical to your operation, the most frequently.
- Testing should be done quickly, using tools that are easy to use and provide accurate readings.
- Use collected test data to determine operating trends and insulation deterioration. Fluke insulation resistance testers that are equipped with Fluke Connect technology eliminate one of the biggest hurdles to implementing a preventive maintenance program — collecting and understanding test data. Until now, technicians have used a “man-meter-pencil” approach to data collection, which has been a deterrent to implementing preventive maintenance programs. Manually written data can be hard to read, contain errors introduced when first recorded, and again when the data is transcribed into a storage system.
- Review insulation resistance test data to determine when service needs to be scheduled for the motor. On Fluke Connect-enabled devices, the technician can set up the test and control the test tool, then, with the push of a button, instantly collect and store relevant results into the cloud for permanent, error-free storage and analysis. In addition, other equipment-specific information is stored with the associated test results: date, time, work order, and more.
Conclusion
Preventive maintenance that includes insulation resistance testing gives maintenance managers more control over electric motor systems. Motor insulation will deteriorate and need service at some point in time; with preventive maintenance, it's up to the maintenance manager to determine just when that is.