Voltage drop is a prevalent electrical issue in modern automotive repair shops. As vehicles incorporate more connections and wiring, their electrical systems become increasingly susceptible to voltage drops. Practicing safe electrical service involves measuring voltage drop before drawing conclusions. Performing a voltage drop test on a circuit can reveal if it's too restricted to operate a component — such as a motor, relay, or light bulb — correctly. If you find a restriction, repair the circuit and retest. If there's no restriction and the component still malfunctions, consider replacing the component.
What is Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop refers to the reduction in electrical potential as current flows through a circuit. It occurs due to resistance in wires, connectors, and other components, which impedes the flow of electricity. In an ideal circuit, all voltage should be delivered to the intended component, but in reality, some energy is lost as heat due to resistance.
A small voltage drop is normal, but excessive voltage drop can cause electrical components to underperform or fail. Technicians need to measure and diagnose voltage drop in order to maintain the efficiency and reliability of automotive and industrial electrical systems.
Symptoms of Voltage Drop
Voltage drop symptoms vary based on the circuit's function and the severity of the drop. Common indicators include dimming headlights, slow cranking during engine start, malfunctioning sensors, and intermittent electrical component failures. These symptoms can be confusing and contradictory, making accurate diagnosis all the more important.
- Inoperative electrical parts
- Sluggish, lazy electrical devices
- Erratic, intermittent devices
- Devices that work sluggishly or erratically during periods of high electrical loads
- Excessive radio interference or noises in the radio
- Damaged throttle or transmission cables or linkage
- Repeated throttle or transmission cable failures
- Damaged drivetrain parts
- Engine or transmission performance complaints
- No starts or hard starts
- High sensor or computer voltages
- Erratic engine or transmission computer performance
- False trouble codes in the memory of any on-board computer
- Premature or repeated A/C compressor clutch failure
This symptom list brings up several points:
- Visual inspections miss most cases of electrical voltage drop. You usually can’t see the corrosion inside a connection or the damaged wire that is causing the problem.
- Ground-side voltage drop, a commonly overlooked cause of electrical trouble, can cause most of these symptoms. Any circuit or component is only as good as its ground.
- The more sophisticated electrical systems become, the more important their grounds are. The number of electrical components has increased rapidly and most do not have separate ground wires. Instead, these devices are grounded to the engine or body. Rust, grease, vibration, and/or careless repairs often restrict the circuit from the engine/body back to the battery.
- Many components, such as engine sensors, share a common ground. Therefore, a bad ground complicates diagnosis because it affects several components at once.
- Some shop manuals and diagnostic charts or fault trees recommend checking grounds last. It is much quicker to check ground circuits before you climb that fault tree.
- It is quicker and smarter to routinely check a circuit’s voltage drop than it is to memorize long lists of symptoms. If experience has taught us nothing else, it is that chasing symptoms is no substitute for routine and thorough voltage drop testing.
There are other reasons to check voltage drop first, too. Voltage drop, usually on the ground side, causes inaccurate or bizarre digital multimeter (DMM) readings and oscilloscope patterns. Moreover, when you connect a digital multimeter or scope to a system with bad grounds, the test equipment itself can create a good substitute ground, depending on the instrument’s impedance. If impedance is low enough, this can be frustrating since your equipment is connected, the circuit works, and you can’t find anything wrong.
Causes of Voltage Drop
Several factors contribute to voltage drop in automotive electrical systems:
- Resistance in conductors: Corrosion, loose connections, or damaged wires can increase resistance, leading to voltage drops.
- Length of wiring: Longer wires have higher resistance, which can cause more significant voltage drops.
- Current load: High-current components, such as starter motors, can cause substantial voltage drops if the wiring isn't adequately sized.
Negative Consequences of Voltage Drop: Why Is It Bad?
Voltage drop can cause a range of performance issues in automotive electrical systems, often leading to frustrating and costly repairs. Here’s why excessive voltage drop is problematic:
1. Reduced component performance
Many electrical components in a vehicle, such as fuel pumps, headlights, and ignition systems, require a consistent voltage to function properly. A significant voltage drop can result in:
- Dim headlights: Reduced brightness affects visibility.
- Weak fuel pump operation: An underperforming pump may lead to poor engine performance or even failure to start.
- Slow or weak cranking: If the starter motor doesn't receive sufficient voltage, the engine may struggle to turn over.
2. Increased heat and potential damage
Excessive resistance in a circuit due to corroded connections, frayed wires, or poor grounding can generate heat. This can cause:
- Wire insulation damage: Overheated wires may melt, shorting circuits.
- Premature component failure: Excess heat can degrade sensitive electronic components, shortening their lifespan.
3. Electrical system instability
Modern vehicles rely heavily on sensors and computer modules. A voltage drop in these systems can result in:
- Erratic sensor readings: Misleading data can trigger false warning lights or cause the engine control unit (ECU) to make incorrect adjustments.
- Malfunctioning electronic systems: Automatic transmissions, anti-lock brakes, and infotainment systems behave unpredictably.
4. Inefficient power distribution
When voltage drops occur in a vehicle’s wiring, other components may try to compensate, leading to:
- Increased current draw: Components pull more current, putting additional strain on the electrical system.
- Battery drain: A struggling alternator and increased electrical demand can drain the battery more quickly, reducing its lifespan.
5. Potential safety hazards
In severe cases, excessive voltage drop can compromise vehicle safety by:
- Disrupting critical safety systems: Airbags, brake lights, and traction control systems may not function as intended.
- Causing electrical fires: If unchecked, high resistance and excessive heat can lead to fire hazards
Calculating Voltage Drop
Understanding how to calculate voltage drop is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues. In direct current (DC) circuits, we apply Ohm's Law:
V = I × R
Where:
- V is the voltage drop
- I is the current in amperes
- R is the resistance in ohms
For example, if a circuit carries 10 amperes through a resistance of 0.5 ohms, the voltage drop would be:
strong>V =10 × 0.5 = 5
This calculation indicates a 5-volt drop across the resistor.
Basic Procedures
Whenever an electrical problem gives you fits, take a deep breath and think of the basic electrical building block: the series circuit. No matter how complicated a system is, you can always simplify it to a smaller series of circuits. Then, inspect each circuit for voltage drop.
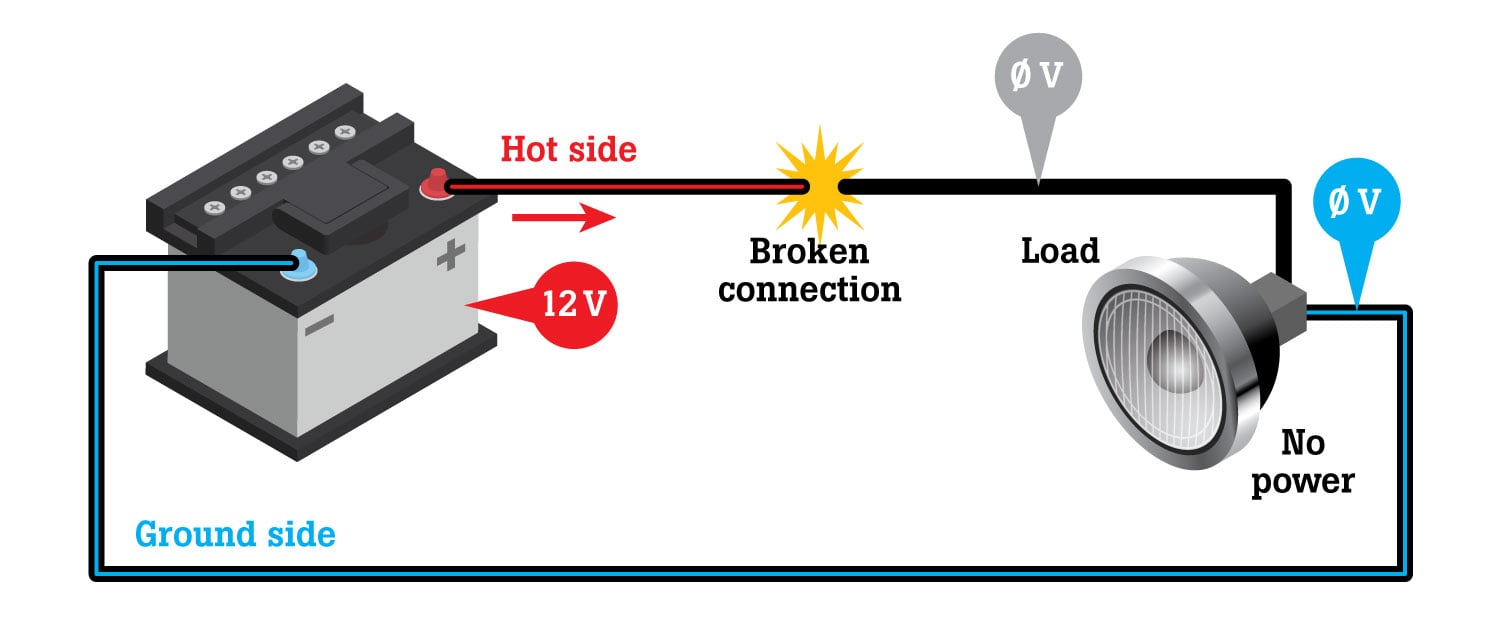
In an electrical circuit, electrical pressure (voltage or volts) pushes electrical volume (current or amps) through the circuit, operating a load. The load may be a computer, a motor, a lamp, a relay, or other device. Electrical pressure (voltage) is used up operating the load. Therefore, voltage falls to about zero on the ground side, but current keeps flowing toward the battery. Because the voltage in a healthy ground circuit should be about zero, some technicians call it ground zero.
Ground-side voltage drop hurts load performance and causes a voltage reading at the ground side of the load.
Resistance and Restriction
Excessive resistance on an electrical circuit can cause a restriction in current flow. Bad connections and broken or undersized wires act like a pipe with a kink, restricting current flow. Restricting current flow anywhere — hot side or ground side — hurts the performance of the load. The effect on the load is hard to predict because it varies with the severity of the restriction. For example, the motor in a restricted circuit may stop working or just run slower than normal.
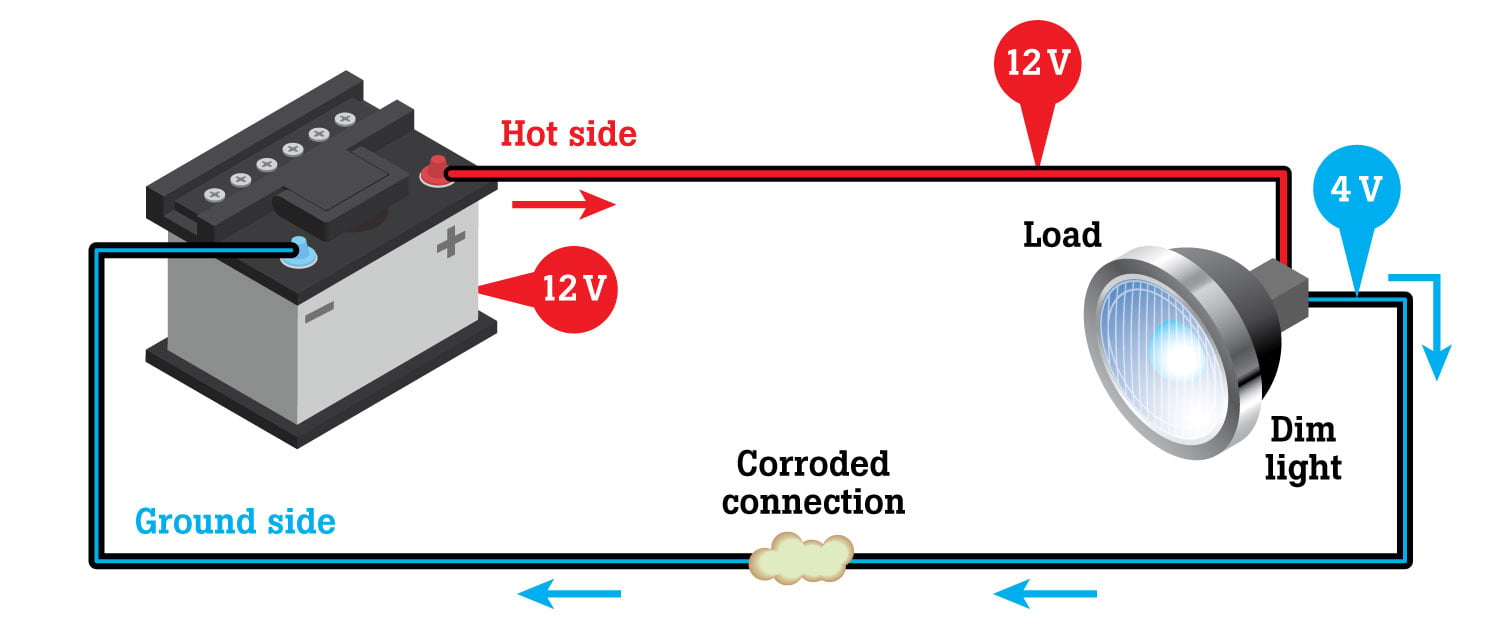
A restricted circuit can cause an A/C compressor clutch to slip and prematurely burn out. A computer on a restricted circuit may shut off or work erratically. When corrosion, loose connections or other types of resistance restrict a circuit, volts and amps both drop. If volts drop, amps drop, too. That is why when you find a voltage drop in a connection or cable, you know the connection or cable is restricted.
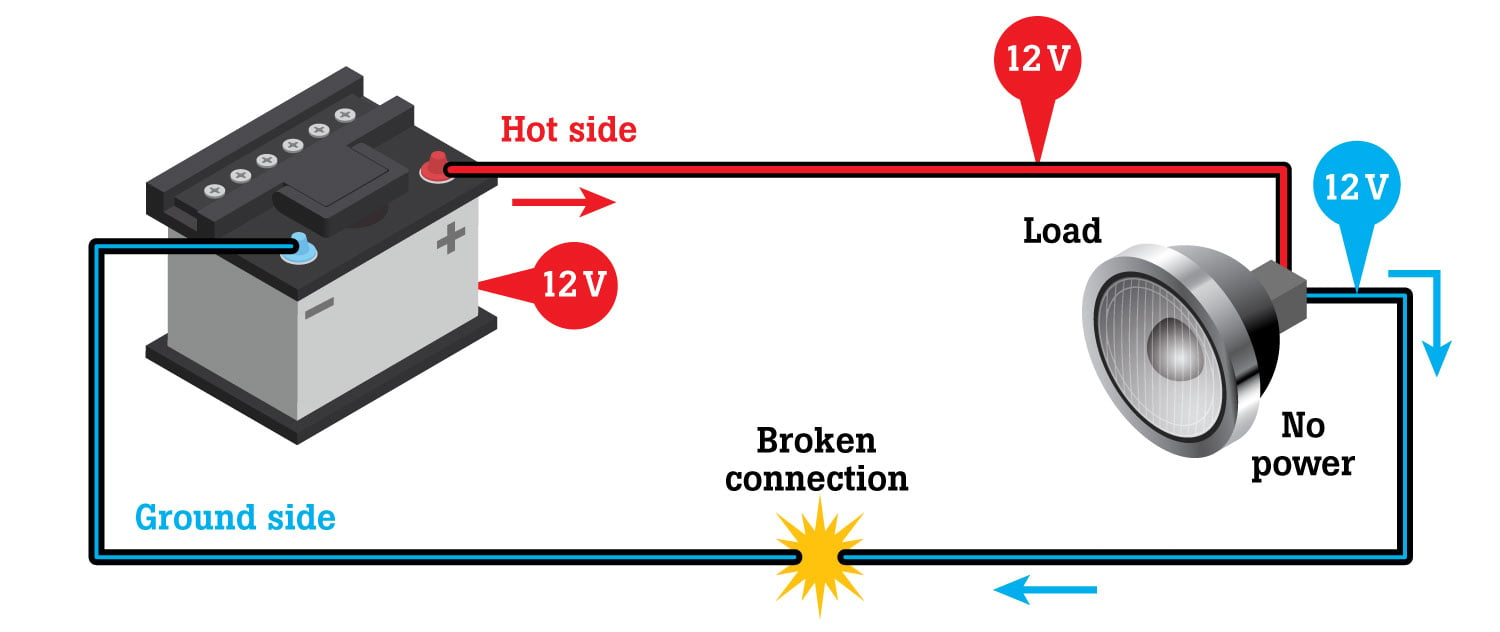
Look at the circuits in our drawings and remember two critical points:
- A free-flowing ground side is as important as a free-flowing hot side.
- A ground-side restriction is the only thing that causes voltage readings greater than 0 to 0.1V in any ground circuit.
A broken ground wire totally blocks current flow, shuts off the load, and causes the ground side of the load to read system voltage.
Voltage Drop Tests
Electrical voltage drop varies according to current flow. Unless you operate the circuit so current flows through it, you cannot measure voltage drop. Because a digital multimeter’s battery cannot supply the current that normally flows through most circuits, digital multimeter tests usually cannot detect restrictions as accurately as a voltage drop test.
Open-circuit problems such as broken or disconnected wires or connections stop current flow. After you fix an open circuit, switch the circuit on again and check for lingering voltage drop. Until you get current flowing and check the circuit again, you cannot know if the entire circuit is healthy.
Although resistance-free connections, wires and cables would be ideal, most of them will contain at least some voltage drop. If your manuals do not list voltage drop values, use the following as maximum limits:
- 0.00V across a connection
- 0.20V across a wire or cable
- 0.30V across a switch
- 0.10V at a ground
Because most computer circuits operate in the milliamp range, they do not tolerate voltage drop as well as other circuits do. Note that a milliamp is one-thousandth (0.001) amp. The recommended working limit is 0.10V-drop across low-current wires and switches. Testing low-current circuits also requires a high-impedance (10-megohm) digital multimeter. A low-impedance digital multimeter may load a low-current circuit so much that it gives an incorrect reading or no reading at all.
Most professional-grade digital multimeters have 10-megohm input impedance. Using a digital multimeter is the fastest way to accurately measure voltage drop. If the digital multimeter you own does not have auto-ranging capability, use a low-voltage (0 to 1V) scale for voltage drop testing. Remember that test lights are not accurate enough to diagnose electrical voltage drop and can damage most computer circuits.
Quick Ground Tests
Because ground circuit voltage drop can cause most of the symptoms listed earlier, consider adopting this new work habit: test grounds first. Before you do a tune-up, check out electrical problems, or test a starting, charging, ABS, or air conditioning system, routinely test the engine and body grounds. Connect your digital multimeter between the engine and negative battery terminal. Safely disarm the ignition and crank the engine for a few seconds, or if your multimeter has a data recording function it will capture the reading in as little as 100 milliseconds.
If the voltage drop is excessive, repair the engine ground circuit and retest. Note that on some ignition systems without a distributor, the simplest way to prevent the engine from starting during the ground test is to pull the fuel pump fuse. Next, connect the digital multimeter between the negative battery terminal and the vehicle’s firewall. Then start the engine and switch on the major electrical accessories. If there is too much voltage drop, then fix the body ground and retest.
Once the engine and body grounds are within limits, proceed with your diagnosis. Do not be surprised if fixing these grounds solves the car’s problems. The fact that a vehicle passes the body ground test does not mean you can safely ground your digital multimeter wherever you want to. Some technicians have run in circles for hours because their digital multimeters were not well grounded. For safe electrical service, make yourself a 20- or 30-foot jumper wire with an alligator clip on each end, allowing you to test an electrical fuel pump, lighting system, or ABS computer in the rear of the vehicle by grounding your digital multimeter to the battery with the jumper wire.
Computer Ground Kinks
Because computer circuits operate on such low current, the standard ground tests may not reveal a marginal ground on an on-board computer. Before you condemn any on-board computer, check its grounds first. Operate the computer system and back-probe each computer ground terminal. If you measure anything greater than 0.10V, trace that ground circuit and locate the problem.
Sometimes, computer grounds are connected to a spot where they are easily disturbed or prone to corrosion, such as a thermostat-housing bolt. Computer connector terminals can also corrode. Removing the connector and spraying the terminals with electrical cleaner may be all it takes to eliminate the voltage drop.
Experience shows that as little as 0.30V on a computer ground terminal can cause trouble. Before pinpointing that with an electronic test light, remember that a traditional test light pulls too much current and can damage the computer. Poor computer and/or sensor grounds can cause higher-than-normal sensor voltages and false trouble codes. In many cases, the bad ground prevents the computer or sensor from pulling a voltage signal down to or near ground zero. Accessing the computer to check grounds may be a hassle. However, mistakenly replacing expensive sensors and computers is a bigger hassle.
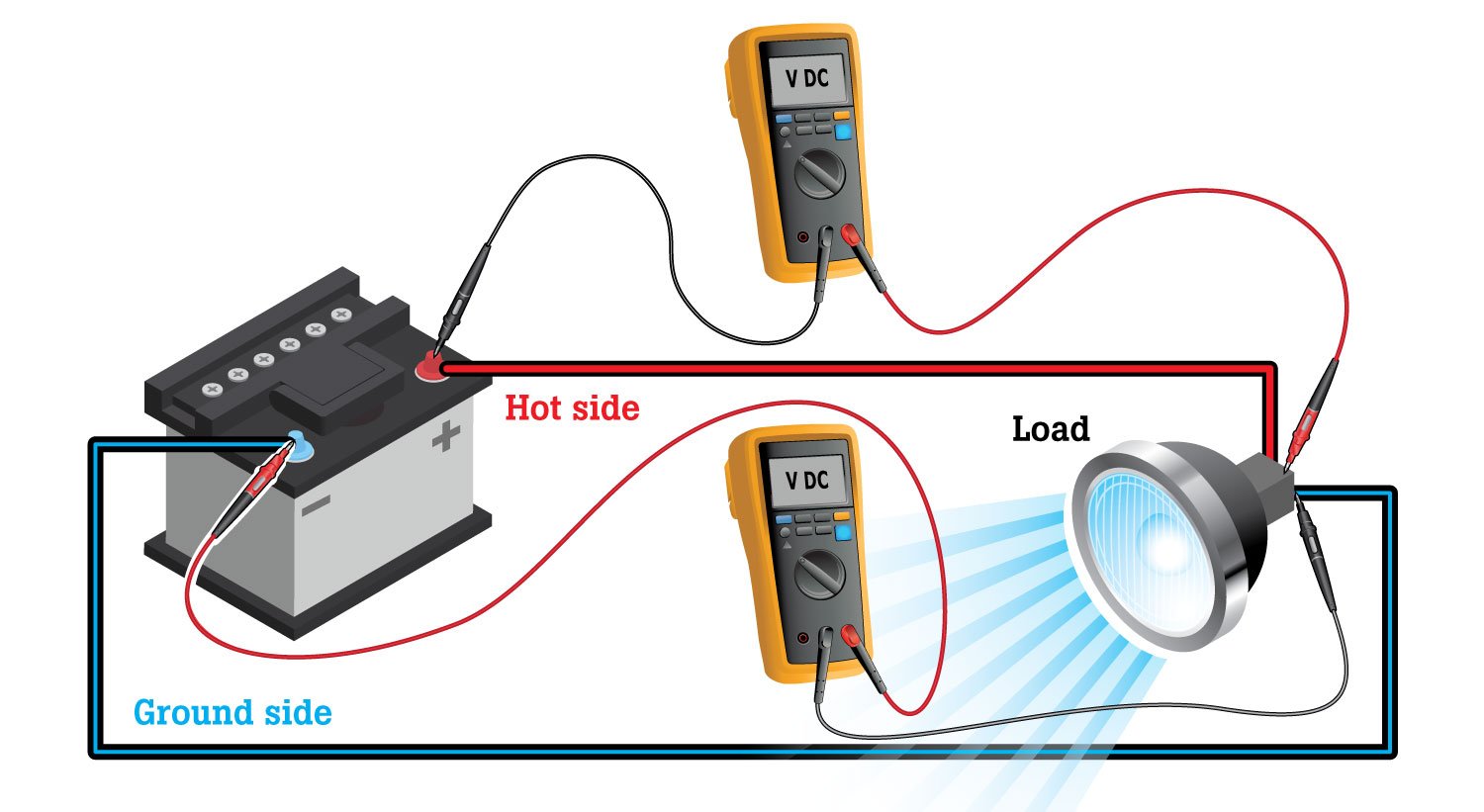
Connect a digital multimeter across any part of a circuit to directly read the voltage drop across that wire, cable, switch, or connection. In this example, one digital multimeter would display the voltage loss between the battery and the load, the other would show the voltage loss from the ground side of the load to the battery.
Body Ground Gremlins
Keep your eyes peeled for missing body grounds. If someone else worked on the vehicle, they may have forgotten to reconnect body ground wires or cables. Remember that when the body ground is restricted, current tries to find another route back to the battery. The easiest alternate route may be through the transmission shift cable or the throttle cable. Not only can this current weld the cable together, it also can pit or erode bushings and bearings inside the transmission or wheel bearings.
If you find the insulation on the body ground wire is burnt or blistered, you can bet that starter current overheated the wire. When the engine ground is restricted, starter current tries to return to the battery through the body ground circuit. Experience shows that if the body ground circuit cannot handle the current load, the customer may not notice the problem right away.
Under periods of heavy current flow, a restricted body ground may hamper or shut off a component. For example, turn signals have been known to stop blinking when the driver steps on the brake pedal. Testing confirmed that a restricted body ground choked off the turn signals. The ground could not handle the current from the turn signals and the brake lights at the same time.
Safe Service
Practicing safe electrical service helps you solve electrical problems quicker and more profitably than guessing and swapping parts out. Put your digital multimeter to work and wipe out electrical voltage drop today. It is the responsible thing to do.
Mitigating Voltage Drop
To avoid the negative consequences of voltage drop, it’s crucial to perform regular electrical system checks, use proper accessories, and keep equipment clean. Testing for voltage drop in key circuits can help identify issues before they escalate into major problems.
To minimize voltage drop in automotive electrical systems:
- Ensure clean connections: Regularly inspect and clean battery terminals, connectors, and grounds to prevent corrosion.
- Use appropriately sized wires: Select wire gauges that can handle the expected current load to reduce resistance.
- Maintain proper grounds: Ensure all ground connections are secure and free from rust or paint, which can impede conductivity.
Keeping Voltage Drop in Check
Voltage drop is a common but critical issue in automotive electrical systems. While a small amount of voltage loss is expected, excessive voltage drop can lead to poor component performance, electrical inefficiencies, and even safety hazards. By understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and using proper diagnostic techniques, technicians can effectively identify and resolve voltage drop issues.
Regular system maintenance, secure connections, and appropriately sized wiring are key to preventing unnecessary voltage loss. Addressing voltage drop proactively ensures that electrical systems function reliably, keeping vehicles operating safely and efficiently.